Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Enhanced Postprocessing#
This updated example demonstrates postprocessing capabilities in PyFluent using an object-oriented approach, providing a more user-friendly interface and improved flexibility. The 3D model used in this example is an exhaust manifold, where high-temperature turbulent flows are analyzed in a conjugate heat transfer scenario.
Key Improvements:
Object-Oriented Design: The code has been modularized into classes and methods, enhancing maintainability and reusability.
Interactive User Interface: The user interface now allows seamless interaction, enabling users to control and customize postprocessing parameters.
Enhanced Plot Interaction: Users have greater freedom to interact with the plots, such as adding and super-imposing multiple plots, and toggling data views, enhancing the visualization experience.
This example utilizes PyVista for 3D visualization and for 2D data plotting. The new design provides a streamlined workflow for exploring and analyzing the temperature and flow characteristics in the exhaust manifold.
Run the following in command prompt to execute this file: exec(open(“updated_post_processing_example.py”).read())
Perform required imports#
Perform required imports and set the configuration.
import ansys.fluent.core as pyfluent
from ansys.fluent.core import examples
from ansys.fluent.core.solver import (
PressureOutlets,
VelocityInlets,
WallBoundaries,
WallBoundary,
using,
)
from ansys.units import VariableCatalog
from ansys.fluent.visualization import (
Contour,
GraphicsWindow,
IsoSurface,
Mesh,
Monitor,
Pathline,
PlaneSurface,
Vector,
XYPlot,
config,
)
pyfluent.CONTAINER_MOUNT_PATH = pyfluent.EXAMPLES_PATH
config.interactive = False
config.view = "isometric"
Download files and launch Fluent#
Download the case and data files and launch Fluent as a service in solver mode with double precision and two processors. Read in the case and data files.
import_case = examples.download_file(
file_name="exhaust_system.cas.h5", directory="pyfluent/exhaust_system"
)
import_data = examples.download_file(
file_name="exhaust_system.dat.h5", directory="pyfluent/exhaust_system"
)
solver_session = pyfluent.launch_fluent(
precision=pyfluent.Precision.DOUBLE,
processor_count=2,
start_transcript=False,
mode=pyfluent.FluentMode.SOLVER,
)
solver_session.settings.file.read_case(file_name=import_case)
solver_session.settings.file.read_data(file_name=import_data)
with using(solver_session):
# Create a graphics object for the mesh display.
graphics_window = GraphicsWindow()
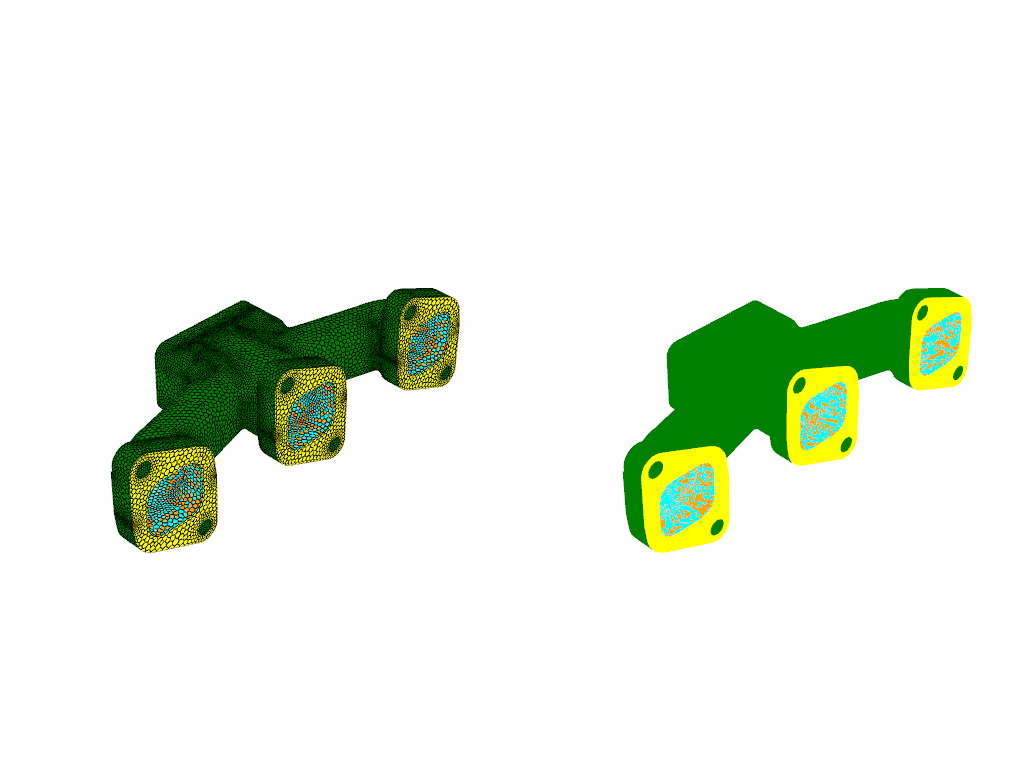
mesh = Mesh(show_edges=True, surfaces=WallBoundaries())
graphics_window.add_graphics(mesh, position=(0, 0))
mesh = Mesh(surfaces=WallBoundaries())
graphics_window.add_graphics(mesh, position=(0, 1))
graphics_window.show()
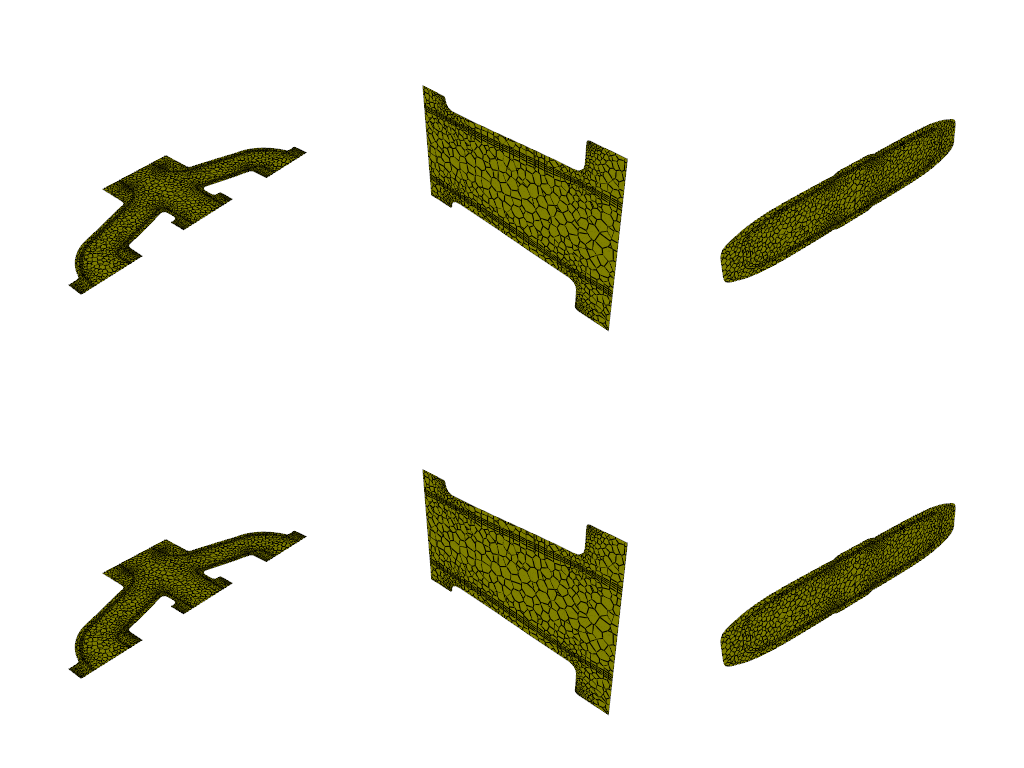
# Create XY, YZ, ZX and an arbitrary plane-surface objects
# from point and normal and display.
graphics_window = GraphicsWindow()
surf_xy_plane = PlaneSurface.create_from_point_and_normal(
point=[0.0, 0.0, -0.0441921], normal=[0.0, 0.0, 1.0]
)
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_xy_plane, position=(0, 0))
surf_yz_plane = PlaneSurface.create_from_point_and_normal(
point=[-0.174628, 0.0, 0.0], normal=[1.0, 0.0, 0.0]
)
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_yz_plane, position=(0, 1))
surf_zx_plane = PlaneSurface.create_from_point_and_normal(
point=[0.0, -0.0627297, 0.0], normal=[0.0, 1.0, 0.0]
)
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_zx_plane, position=(0, 2))
# Create XY, YZ and ZX plane-surface objects and display.
surf_xy_plane = PlaneSurface.create_xy_plane(z=-0.0441921)
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_xy_plane, position=(1, 0))
surf_yz_plane = PlaneSurface.create_yz_plane(x=-0.174628)
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_yz_plane, position=(1, 1))
surf_zx_plane = PlaneSurface.create_zx_plane(y=-0.0627297)
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_zx_plane, position=(1, 2))
graphics_window.show()
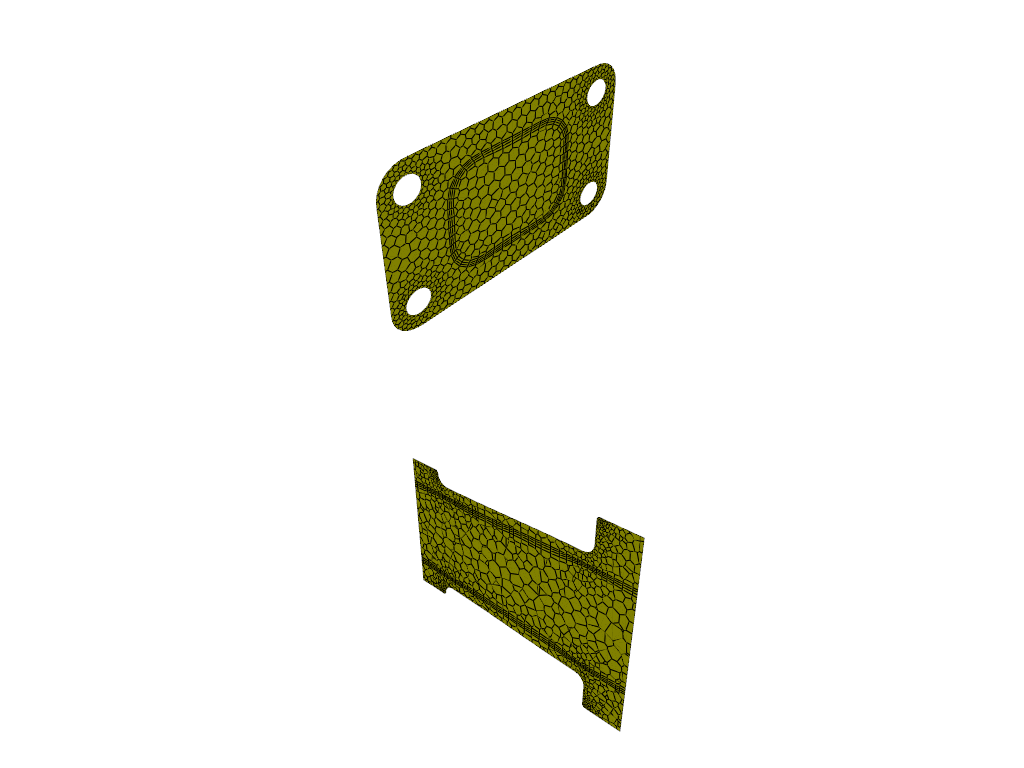
# Create an iso-surface on the outlet and mid-plane.
graphics_window = GraphicsWindow()
surf_outlet_plane = IsoSurface(field="y-coordinate", iso_value=-0.125017)
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_outlet_plane, position=(0, 0))
surf_mid_plane_x = IsoSurface(field="x-coordinate", iso_value=-0.174)
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_mid_plane_x, position=(1, 0))
graphics_window.show()
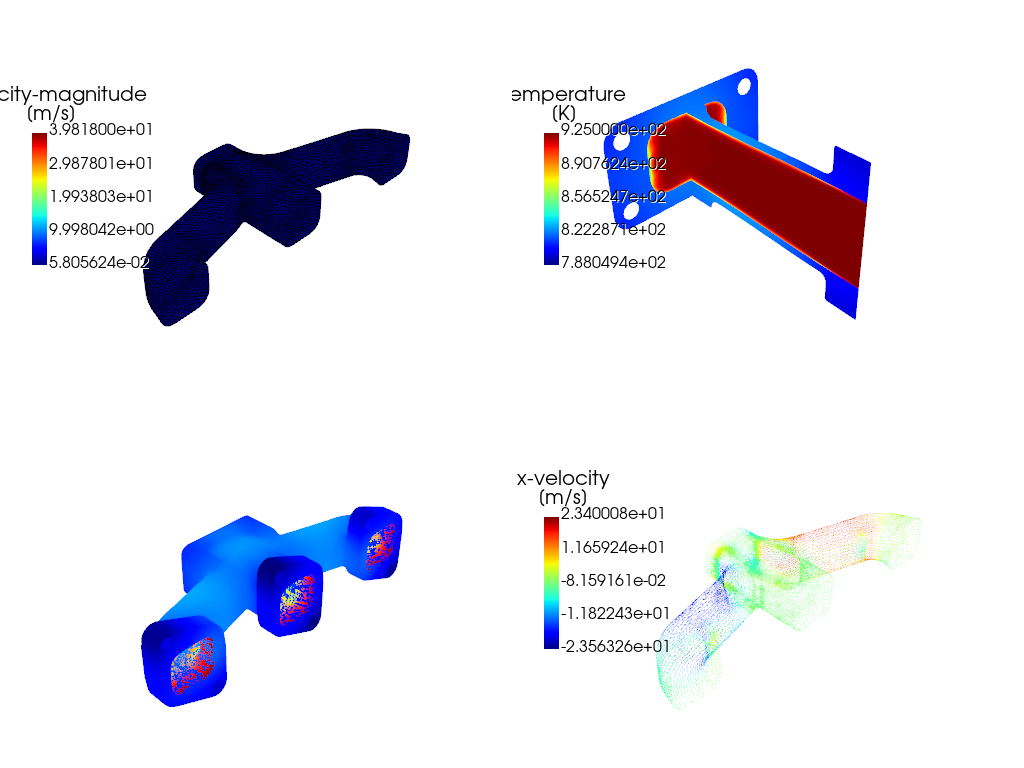
# Create an iso-surface using the velocity magnitude, a temperature contour
# on the mid-plane and the outlet, a contour plot of the temperature on the
# manifold and a vector on a predefined surface.
graphics_window = GraphicsWindow()
surf_vel_contour = IsoSurface(
field=VariableCatalog.VELOCITY_MAGNITUDE, rendering="contour", iso_value=0.0
)
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_vel_contour)
temperature_contour = Contour(
field=VariableCatalog.TEMPERATURE,
surfaces=[surf_mid_plane_x.name, surf_outlet_plane.name],
)
graphics_window.add_graphics(temperature_contour, position=(0, 1))
temperature_contour_manifold = Contour(
field=VariableCatalog.TEMPERATURE, surfaces=WallBoundaries()
)
graphics_window.add_graphics(temperature_contour_manifold, position=(1, 0))
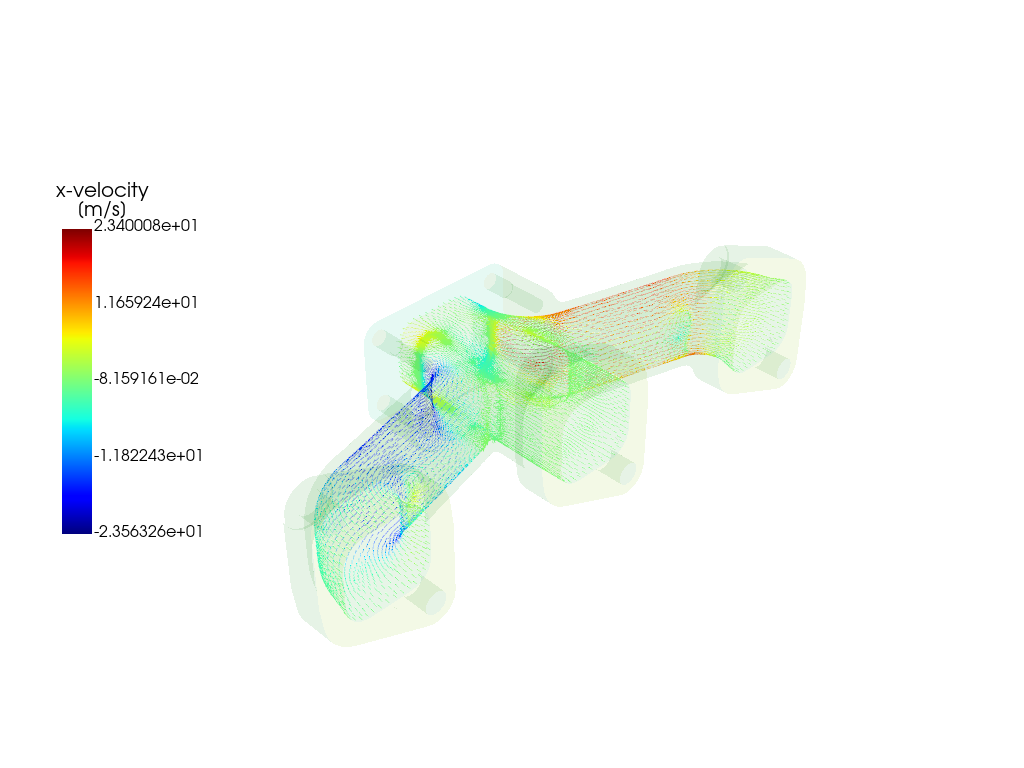
velocity_vector = Vector(
field=VariableCatalog.VELOCITY_X,
surfaces=[WallBoundary(name="solid_up:1:830")],
scale=20,
)
graphics_window.add_graphics(velocity_vector, position=(1, 1))
graphics_window.show()
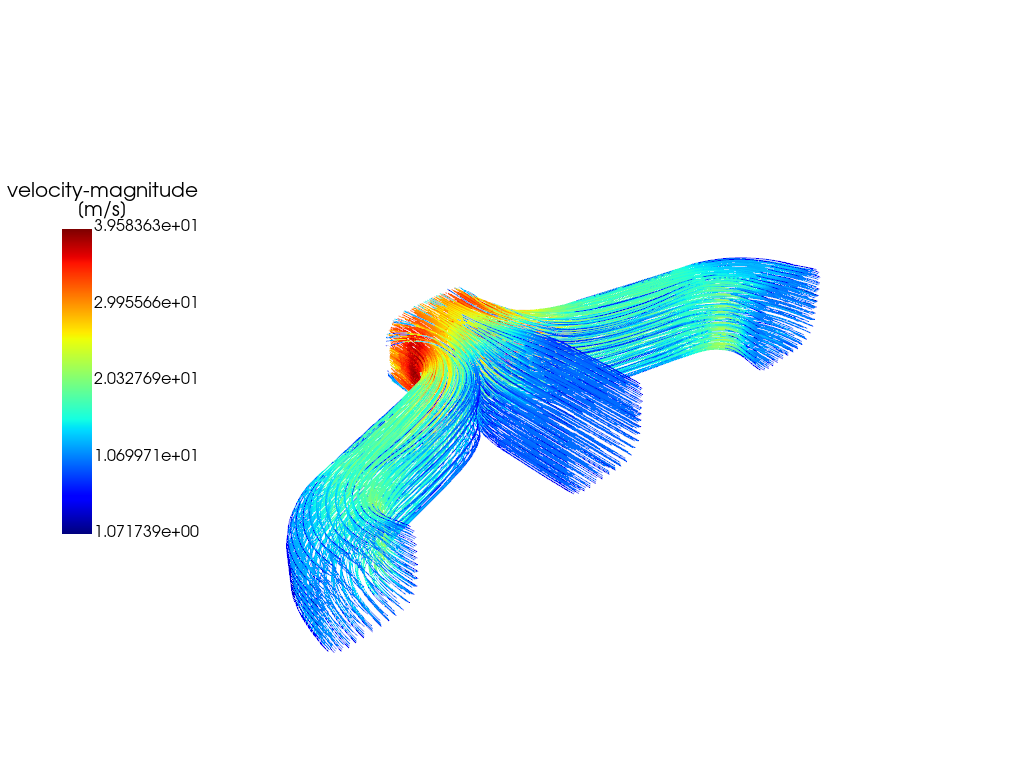
# Create a pathlines on a predefined surface.
graphics_window = GraphicsWindow()
pathlines = Pathline(
field=VariableCatalog.VELOCITY_MAGNITUDE, surfaces=VelocityInlets()
)
graphics_window.add_graphics(pathlines)
graphics_window.show()
# Create a combined mesh and vector plot by varying opacity.
graphics_window = GraphicsWindow()
graphics_window.add_graphics(mesh, opacity=0.05)
graphics_window.add_graphics(velocity_vector)
graphics_window.show()
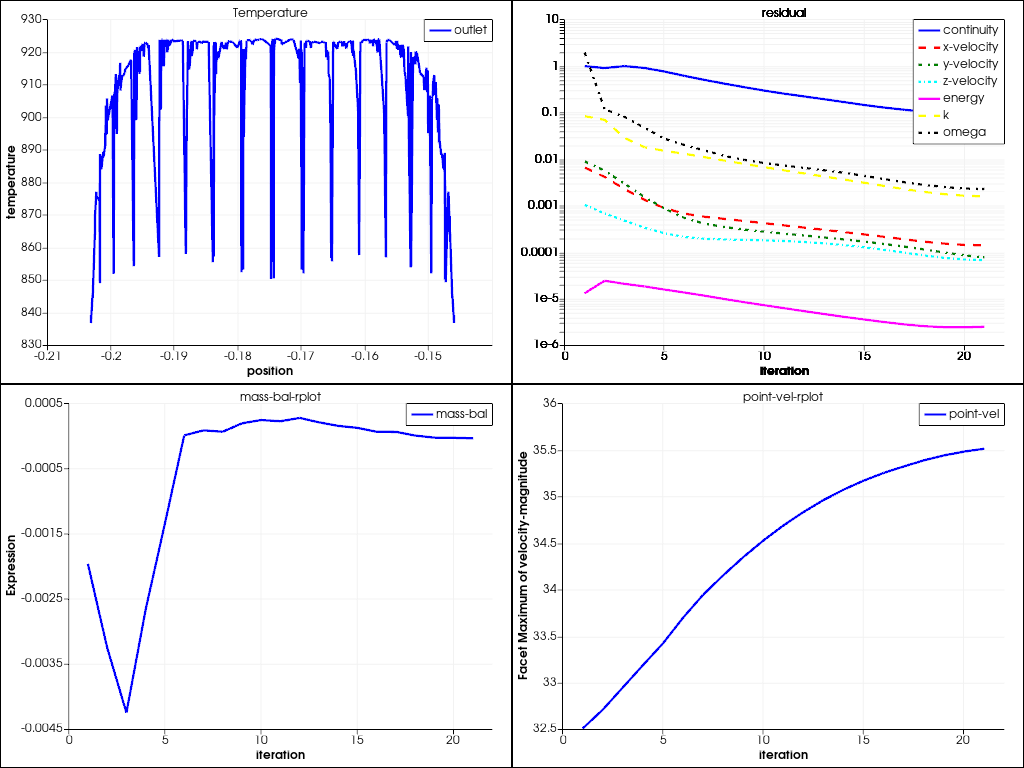
# Create and display XY plot, residual plot and solve and plot solution monitors.
plot_window = GraphicsWindow()
xy_plot_object = XYPlot(
surfaces=PressureOutlets(), y_axis_function=VariableCatalog.TEMPERATURE
)
plot_window.add_plot(xy_plot_object, position=(0, 0), title="Temperature")
residual = Monitor(monitor_set_name="residual")
plot_window.add_plot(residual, position=(0, 1))
solver_session.solution.initialization.hybrid_initialize()
solver_session.solution.run_calculation.iterate(iter_count=50)
mass_bal_rplot = Monitor(monitor_set_name="mass-bal-rplot")
plot_window.add_plot(mass_bal_rplot, position=(1, 0))
point_vel_rplot = Monitor(monitor_set_name="point-vel-rplot")
plot_window.add_plot(point_vel_rplot, position=(1, 1))
plot_window.show()
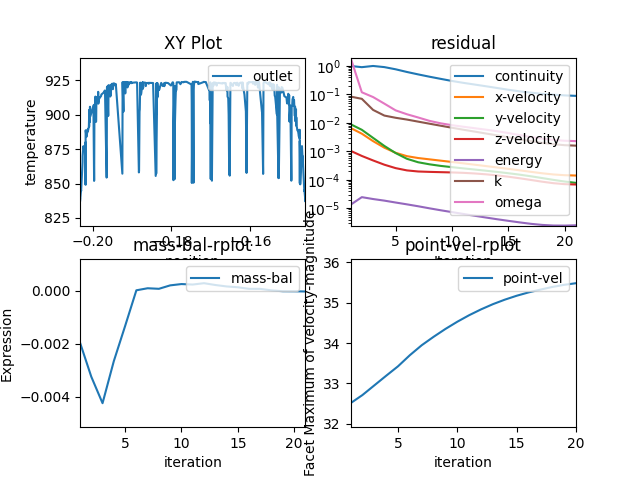
plot_window.renderer = "matplotlib"
plot_window.show()
Total running time of the script: (2 minutes 33.677 seconds)