Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Post-processing using Pyvista and Matplotlib#
This example shows how to use PyFluent’s post-processing tools to visualize Fluent results in both 3D and 2D. It demonstrates a typical workflow for exploring simulation data—such as temperature and velocity fields—using Pyvista for interactive 3D graphics and Matplotlib for standard 2D plots.
The model used here is an exhaust manifold, but the techniques apply to any Fluent simulation.
What this example demonstrates
3D Visualization with Pyvista: Display meshes, surfaces, iso-surfaces, contours, vectors, and pathlines to understand spatial flow behavior.
2D Plotting with Matplotlib: Create XY plots such as temperature or velocity profiles, monitor quantities, and compare numerical trends.
Simple, Practical Workflow: Shows how to load results, create common visualization objects, adjust display settings, and interact with the scene — all with clear, straightforward commands.
Unified Post-Processing Interface: Combines 3D and 2D visualization tools so users can inspect their results from multiple perspectives within a single, consistent workflow.
This example provides a concise starting point for analyzing Fluent simulations visually, without requiring knowledge of internal APIs or implementation details.
Perform required imports#
Perform required imports and set the configuration.
import ansys.fluent.core as pyfluent
from ansys.fluent.core import examples
from ansys.units import VariableCatalog
from ansys.fluent.visualization import (
Contour,
GraphicsWindow,
Mesh,
Monitor,
Pathline,
Surface,
Vector,
XYPlot,
config,
)
pyfluent.CONTAINER_MOUNT_PATH = pyfluent.EXAMPLES_PATH
config.interactive = False
config.view = "isometric"
Download files and launch Fluent#
Download the case and data files and launch Fluent as a service in solver mode with double precision and two processors. Read in the case and data files.
import_case = examples.download_file(
file_name="exhaust_system.cas.h5", directory="pyfluent/exhaust_system"
)
import_data = examples.download_file(
file_name="exhaust_system.dat.h5", directory="pyfluent/exhaust_system"
)
solver_session = pyfluent.launch_fluent(
precision=pyfluent.Precision.DOUBLE,
processor_count=2,
start_transcript=False,
mode=pyfluent.FluentMode.SOLVER,
)
solver_session.settings.file.read_case(file_name=import_case)
solver_session.settings.file.read_data(file_name=import_data)
Create graphics object for mesh display#
Create a graphics object for the mesh display.
mesh_surfaces_list = [
"in1",
"in2",
"in3",
"out1",
"solid_up:1",
"solid_up:1:830",
"solid_up:1:830-shadow",
]
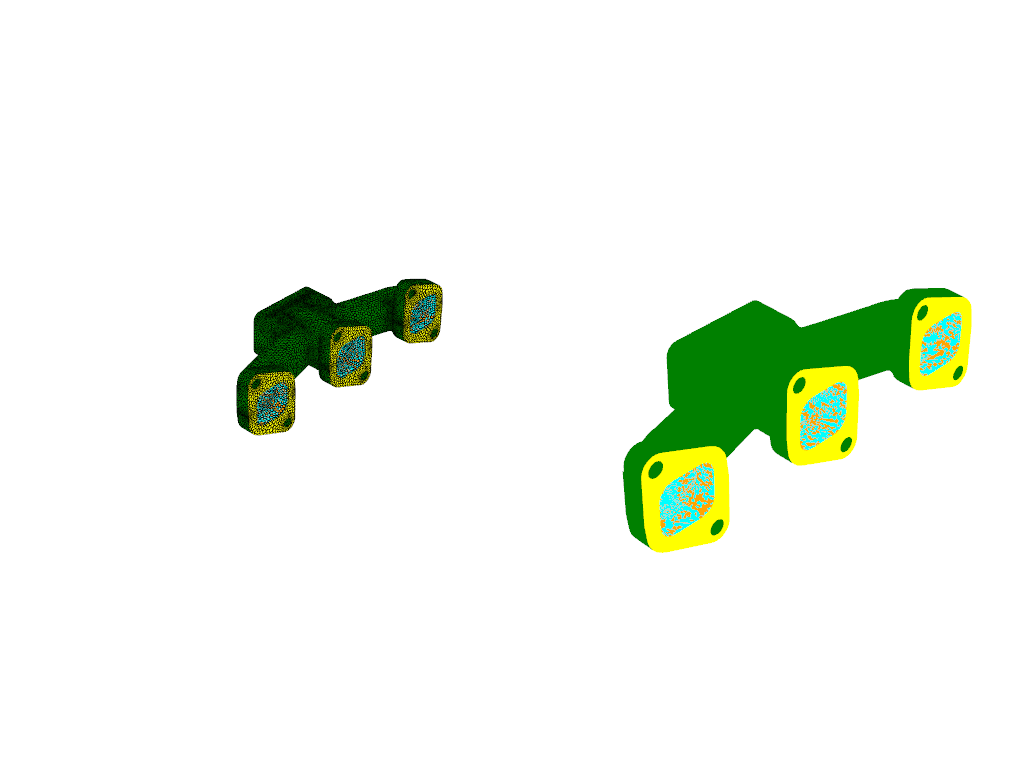
mesh = Mesh(solver=solver_session, show_edges=True, surfaces=mesh_surfaces_list)
graphics_window = GraphicsWindow()
graphics_window.add_graphics(mesh, position=(0, 0))
mesh = Mesh(solver=solver_session, surfaces=mesh_surfaces_list)
graphics_window.add_graphics(mesh, position=(0, 1))
graphics_window.show()
Create plane-surface XY plane#
Create a plane-surface XY plane.
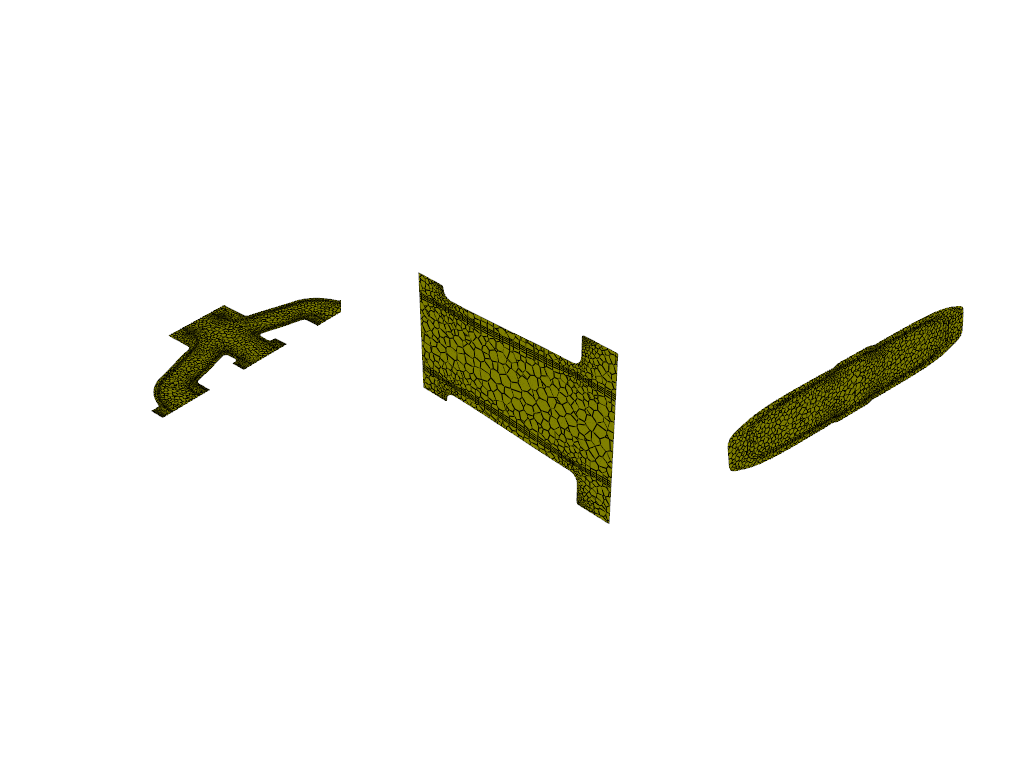
surf_xy_plane = Surface(
solver=solver_session,
type="plane-surface",
creation_method="xy-plane",
z=-0.0441921,
)
graphics_window = GraphicsWindow()
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_xy_plane, position=(0, 0))
Create plane-surface YZ plane#
Create a plane-surface YZ plane.
surf_yz_plane = Surface(
solver=solver_session, type="plane-surface", creation_method="yz-plane", x=-0.174628
)
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_yz_plane, position=(0, 1))
Create plane-surface ZX plane#
Create a plane-surface ZX plane.
surf_zx_plane = Surface(
solver=solver_session,
type="plane-surface",
creation_method="zx-plane",
y=-0.0627297,
)
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_zx_plane, position=(0, 2))
graphics_window.show()
Create iso-surface on outlet plane#
Create an iso-surface on the outlet plane.
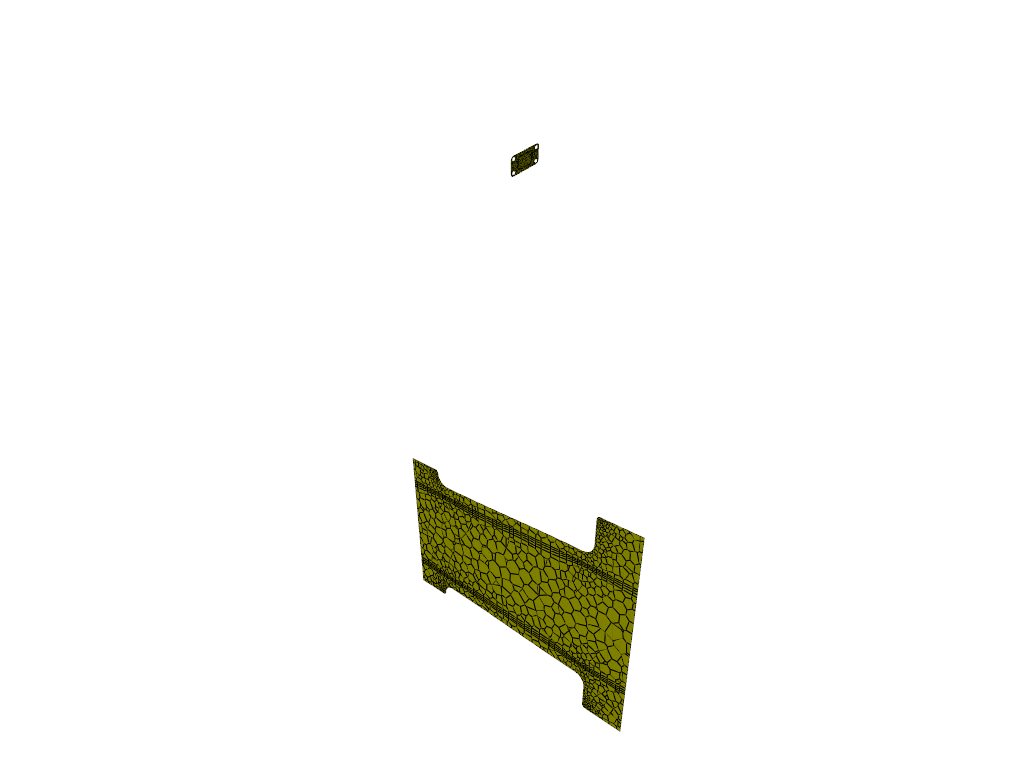
surf_outlet_plane = Surface(solver=solver_session, type="iso-surface")
surf_outlet_plane.field = "y-coordinate"
surf_outlet_plane.iso_value = -0.125017
graphics_window = GraphicsWindow()
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_outlet_plane, position=(0, 0))
Create iso-surface on mid-plane#
Create an iso-surface on the mid-plane.
surf_mid_plane_x = Surface(
solver=solver_session, type="iso-surface", field="x-coordinate", iso_value=-0.174
)
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_mid_plane_x, position=(1, 0))
graphics_window.show()
Create iso-surface using velocity magnitude#
Create an iso-surface using the velocity magnitude.
surf_vel_contour = Surface(
solver=solver_session,
type="iso-surface",
field="velocity-magnitude",
rendering="contour",
iso_value=0.0,
)
graphics_window = GraphicsWindow()
graphics_window.add_graphics(surf_vel_contour, position=(0, 0))
Create temperature contour on mid-plane and outlet#
Create a temperature contour on the mid-plane and the outlet.
temperature_contour = Contour(
solver=solver_session,
field="temperature",
surfaces=[surf_mid_plane_x.name, surf_outlet_plane.name],
)
graphics_window.add_graphics(temperature_contour, position=(0, 1))
Create contour plot of temperature on manifold#
Create a contour plot of the temperature on the manifold.
cont_surfaces_list = [
"in1",
"in2",
"in3",
"out1",
"solid_up:1",
"solid_up:1:830",
]
temperature_contour_manifold = Contour(
solver=solver_session,
field=VariableCatalog.TEMPERATURE,
surfaces=cont_surfaces_list,
)
graphics_window.add_graphics(temperature_contour_manifold, position=(1, 0))
Create vector#
Create a vector on a predefined surface.
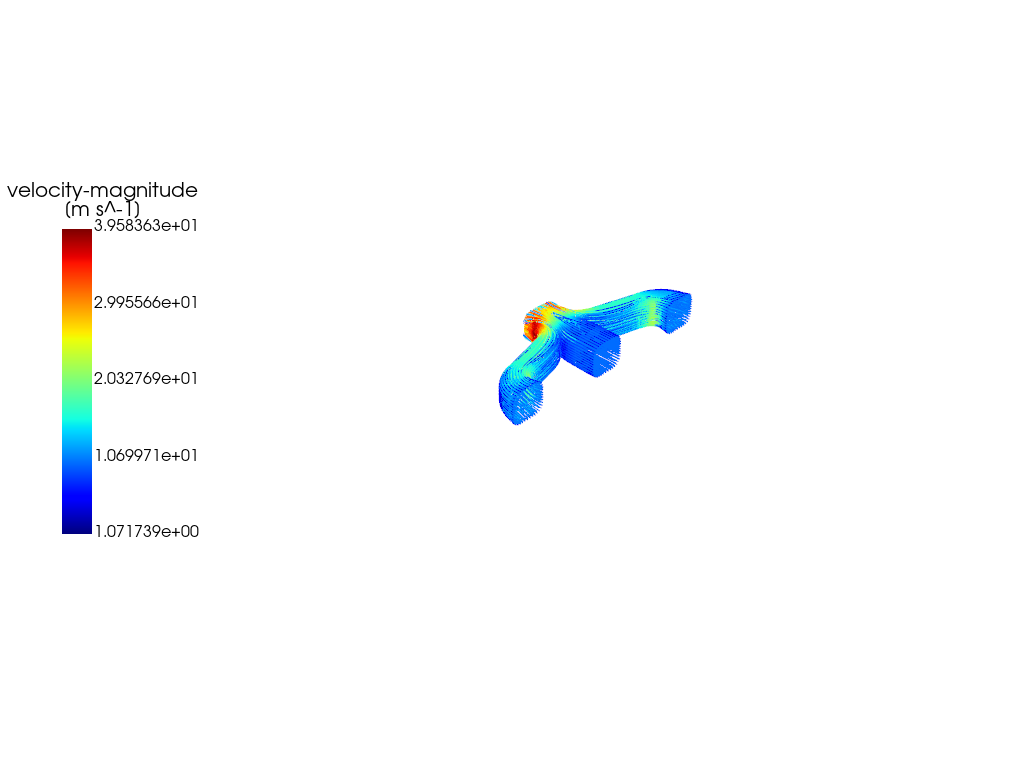
velocity_vector = Vector(
solver=solver_session,
field="velocity",
color_by="x-velocity",
surfaces=["solid_up:1:830"],
scale=20,
)
graphics_window.add_graphics(velocity_vector, position=(1, 1))
graphics_window.show()

Create Pathlines#
Create a pathlines on a predefined surface.
pathlines = Pathline(
solver=solver_session,
field="velocity-magnitude",
surfaces=["inlet", "inlet1", "inlet2"],
)
graphics_window = GraphicsWindow()
graphics_window.add_graphics(pathlines)
graphics_window.show()
graphics_window = GraphicsWindow()
graphics_window.add_graphics(mesh, opacity=0.05)
graphics_window.add_graphics(velocity_vector)
graphics_window.show()
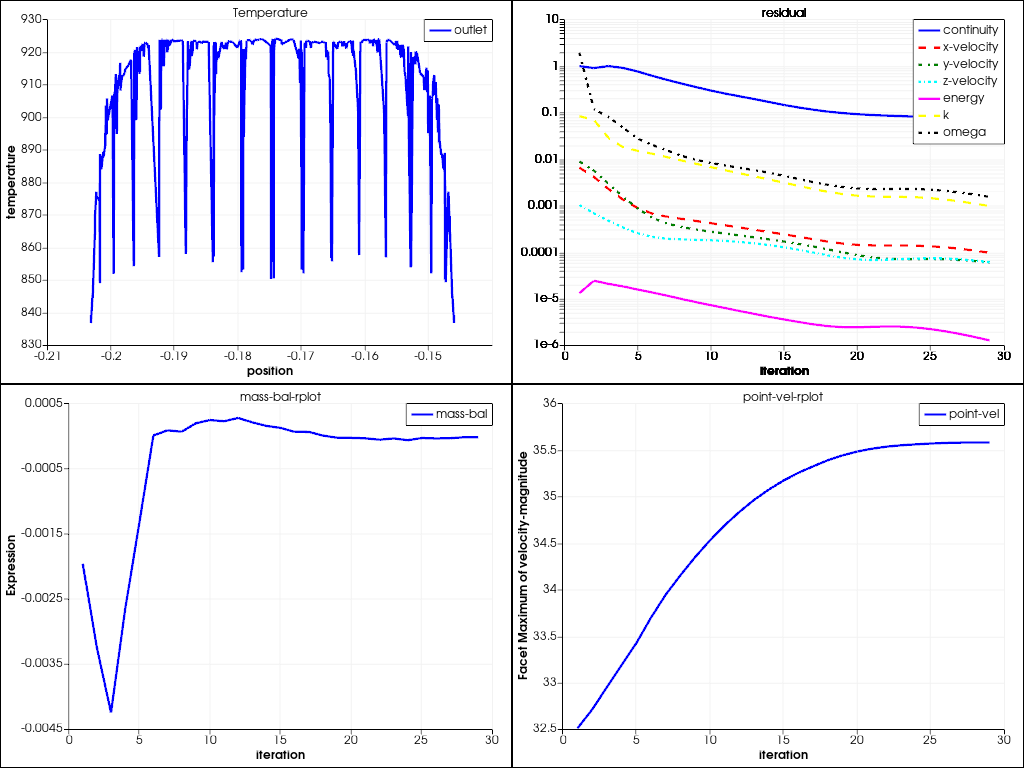
Create XY plot#
Create the default XY plot.
xy_plot_object = XYPlot(
solver=solver_session,
surfaces=["outlet"],
y_axis_function="temperature",
)
plot_window = GraphicsWindow()
plot_window.add_plot(xy_plot_object, position=(0, 0), title="Temperature")
Create residual plot#
Create and display the residual plot.
residual = Monitor(solver=solver_session, monitor_set_name="residual")
plot_window.add_plot(residual, position=(0, 1))
Solve and plot solution monitors#
Solve and plot solution monitors.
solver_session.solution.initialization.hybrid_initialize()
solver_session.solution.run_calculation.iterate(iter_count=50)
mass_bal_rplot = Monitor(solver=solver_session, monitor_set_name="mass-bal-rplot")
plot_window.add_plot(mass_bal_rplot, position=(1, 0))
point_vel_rplot = Monitor(solver=solver_session, monitor_set_name="point-vel-rplot")
plot_window.add_plot(point_vel_rplot, position=(1, 1))
plot_window.show()
Close Fluent#
Close Fluent.
solver_session.exit()
del solver_session
Total running time of the script: (2 minutes 41.437 seconds)